TiN coating
Perfect surfaces with titanium nitride
Are you looking for a reliable way to improve the durability and performance of your tools? TiN coating (titanium nitride coating) can offer just that. Behind the brilliance of titanium nitride is a history of versatility, top performance and impressive functionality - a success story that has made it an indispensable part of PVD coating technology.
What is a TiN coating?
TiN, or titanium nitride, is a chemical compound consisting of titanium and nitrogen that is commonly used as a coating in metalworking. This compound combines the hardness of titanium with the chemical stability of nitrogen, making it ideal for applications that require high wear resistance. Tin titanium nitride is another interesting variant in this area.
The TiN coating is often used synonymously with PVD coatings, as it is applied using the PVD process. This process makes it possible to produce extremely thin and uniform layers that are extremely hard and durable. The use of TiN in coatings has proven to be extremely effective in extending the life and improving the performance of tools and components.
TiN coatings are used in many industries, from metalworking and plastics processing to medical implants. The versatility and excellent properties of this coating make it a preferred choice for many different applications.
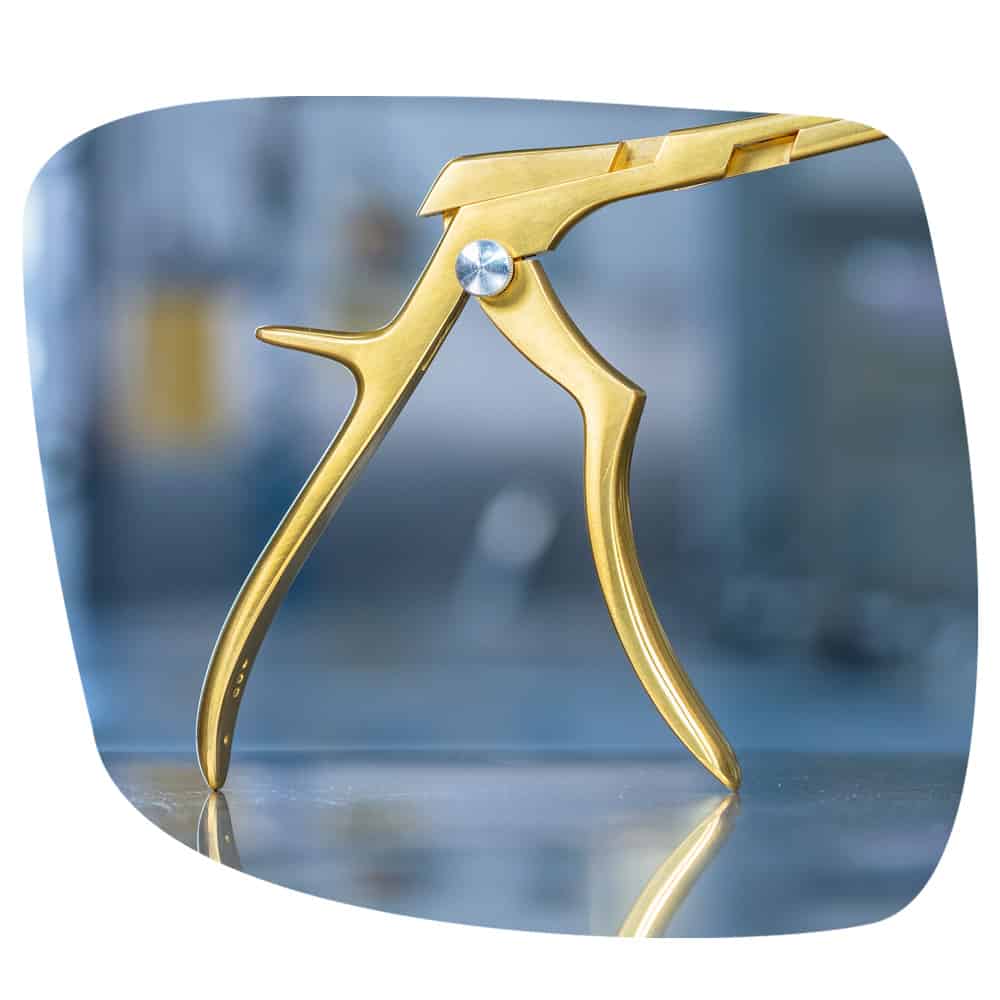

Physical properties
The TiN coating has a remarkable hardness of around 2400 HV, which makes it extremely resistant to scratches and abrasion. This high hardness exceeds that of many metallic materials and makes TiN an ideal choice for applications that require high wear resistance.
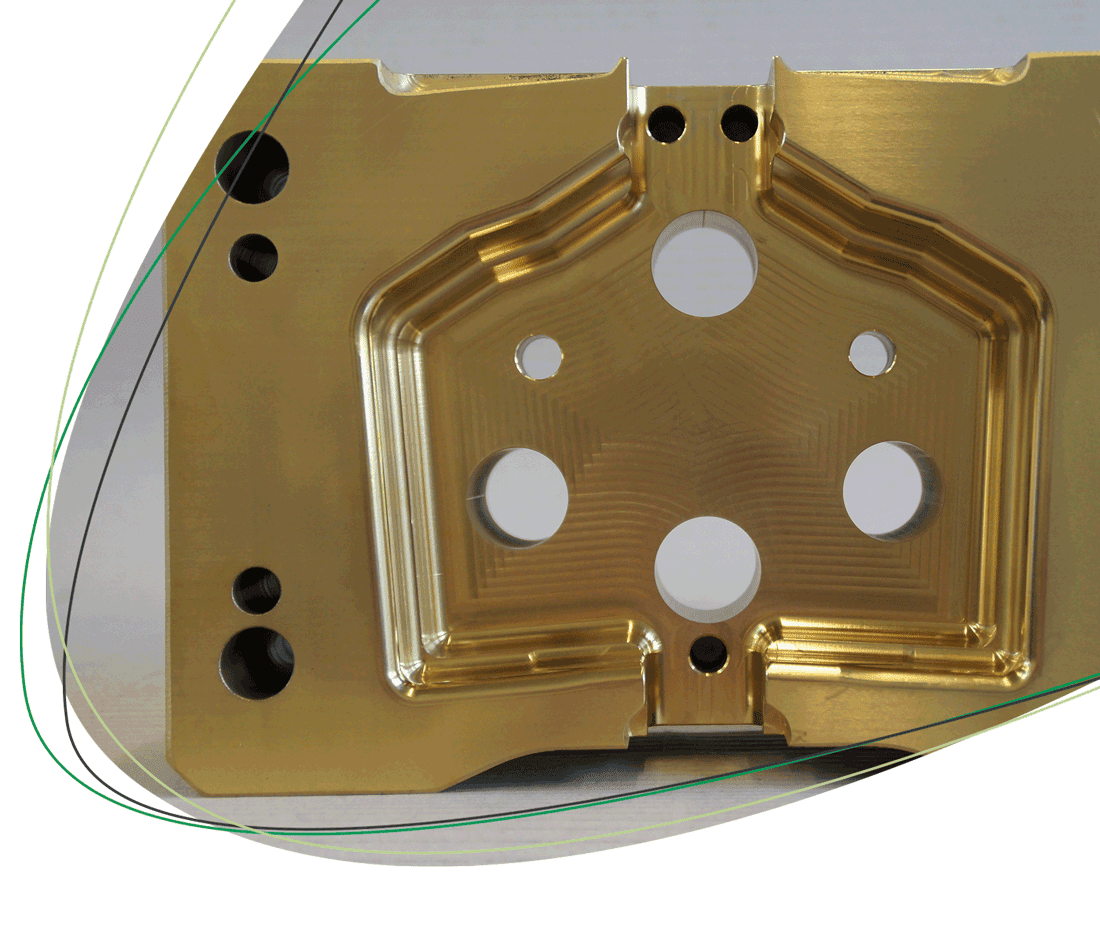
The color of the TiN coating is characteristically gold or yellowish, which makes it easily recognizable and gives it an aesthetically pleasing appearance. This color is due to the specific crystal structure and the metallic properties of titanium nitride. TiN has a maximum application temperature of 600 °C, above which the coating begins to erode. The melting point of titanium nitride is around 2930 °C, which makes it suitable for high-temperature applications.
The coefficient of friction of TiN is around 0.55, which influences the efficiency of the machined materials. With a density of 5.22 g/cm³ and a thermal conductivity of around 30 W/m-K, TiN has a high temperature resistance and is not significantly attacked in air before 600 °C.
Chemical composition
The chemical composition of the TiN coating consists of a combination of titanium (Ti) and nitrogen (N), with the ratio typically being 1:1. This stable chemical composition gives the TiN coating its remarkable properties, such as high hardness and chemical resistance.
The chemical formula for titanium nitride, TiN, reflects this composition. This simple but effective combination makes TiN an ideal material for coatings used in many industrial applications.
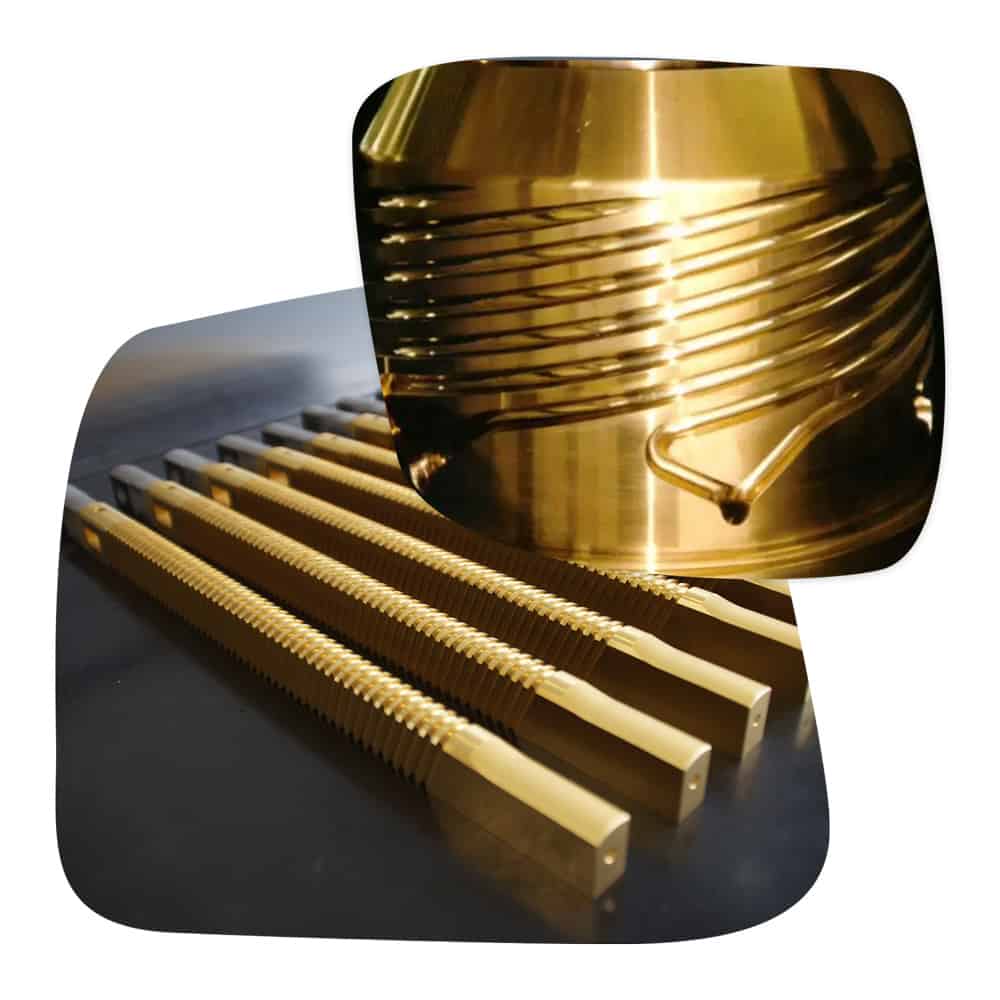

TiN coating - The best choice for your application
TiN, or titanium nitride, is a chemical compound consisting of titanium and nitrogen that is widely used in metalworking. This compound combines the hardness of titanium with the chemical stability of nitrogen, making it an ideal choice for PVD coatings. TiN coating, also known as titanium nitride coating, offers excellent resistance to wear and corrosion, making it interesting for a wide range of applications.
PVD, or physical vapor deposition, is a process that is often used to produce these coatings. In this process, the target material is vaporized by electric arcs and applied to the workpiece to be coated. This technology makes it possible to produce extremely thin and uniform coatings that are extremely hard and durable.
The versatility of TiN coating is reflected in its numerous areas of application. From metalworking and plastics processing to medical implants, TiN coating offers significant benefits in many industries. It not only extends the service life of tools, but also improves their performance and efficiency by reducing wear and increasing surface hardness.
The combination of hardness, chemical stability and biocompatibility makes the TiN coating an excellent choice for many industrial applications. Whether you need tools for machining, injection molds for plastics processing or medical implants, TiN coating offers a reliable and effective solution.
PVD coating technology
The technology used to produce the TiN coating is the arc evaporation technique, also known as PVD coating. This method makes it possible to produce extremely thin and uniform coatings that have high hardness and resistance. PVD, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is a process in which the target material is vaporized by electric arcs and applied to the workpiece. This technique is often used to produce TiN coatings that have excellent wear resistance and biocompatibility.
How PVD technology works
In PVD coating, the target material is vaporized by an electric arc in order to apply it to the workpiece. The process takes place in an evacuated high-vacuum chamber into which nitrogen and other reactive gases are added to create the desired chemical compound.
By adjusting suitable reactive gases, temperatures and machine parameters, the chemical composition of the PVD coating can be precisely controlled. This flexibility makes it possible to produce coatings that are specifically tailored to the requirements of the respective application.
ARC evaporation technology makes it possible to apply TiN coatings to implants and other workpieces, significantly improving their performance and service life.
Advantages of PVD coating
PVD coatings do not use toxic or polluting substances, making them an environmentally friendly option. These coatings are characterized by ultra-thin layers with a natural metallic look that are both aesthetically pleasing and functional.
GPA Coatings has a long history of developing innovative coating technologies that support the performance of PVD coatings. These technologies are critical to improving the performance of various tools and components.
PVD coating technology offers numerous benefits, including increased wear resistance, extended tool life and improved performance in various applications.
Machining
In machining, the choice of the right coating thickness plays a decisive role in the performance of TiN-coated tools. Thinner coatings are beneficial for less hard materials, while harder materials require a thinner coating for optimal results. The right coating thickness can significantly extend tool life and improve efficiency.
The TiN coating is often used in the machining of materials such as steel, brass and cast iron to increase the service life of tools. This coating offers an excellent combination of hardness and wear protection, which is essential for metalworking.
Plastics processing
In plastics processing, TiN coating can significantly increase tool life and efficiency. TiN coatings improve tool performance in plastic injection molding by reducing friction when abrasive components (e.g. glass fiber) are injected, thus extending the life of the tool.
In addition, the TiN coating improves the demoulding of injection molds, resulting in higher product quality and lower reject rates. The combination of hardness and chemical resistance makes TiN an ideal choice for plastics processing.
Medical implants
TiN coatings offer excellent biocompatibility, making them ideal for medical applications. These coatings reduce the release of allergenic metals such as nickel, cobalt and chromium, which minimizes the risk of allergic reactions in patients.
In clinical studies, TiN-coated implants show no evidence of allergic reactions, which underlines their safety and tolerability. These properties make TiN a preferred choice for medical implants.
Advantages of the TiN coating
The TiN coating offers numerous advantages, including high hardness, chemical stability and biocompatibility. This coating significantly extends the life of tools and components and improves their performance by reducing wear. GPA Coatings offers environmentally friendly PVD coating technology that increases the wear resistance and durability of tools. These coatings are used in many industries, including the food industry, due to their high chemical resistance and food safety.
Wear protection
TiN coatings are particularly wear-resistant due to their high hardness. With a hardness of up to 2,000 HV, TiN is particularly effective as wear protection in tools. A hardness of up to 2,000 HV means that the material has a Vickers hardness of up to 2,000 HV.
Vickers hardness (HV)
Vickers hardness (HV) is a measure of the resistance of a material to penetration by a special diamond indenter and is expressed in HV. Up to 2,000 HV means that the material is extremely hard and is particularly suitable for applications where high wear resistance is required.
The abrasion rate of TiN-coated components is only 38% compared to uncoated CoCrMo components. This low abrasion rate significantly extends the service life of the tools and improves their performance.
Minimized ion emission
The application of TiN coating minimizes the release of allergenic ions from metallic implants. TiN acts as a barrier and minimizes the release of nickel, cobalt and chromium, which reduces the risk of allergic reactions.
These properties make TiN particularly suitable for medical devices and implants, as it offers excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance.
Aesthetics and toughness
TiN coatings are known for their high hardness and chemical stability at high temperatures. With a nano-hardness of up to 2,000 HV, TiN offers exceptional wear resistance and durability.
In addition to their functional advantages, surfaces coated with PVD technology have fascinating metallic and visually attractive shades that make them aesthetically pleasing.
Layer thickness and its significance
The thickness of the TiN coating typically varies between 1 2 and 7 10 micrometers. This thickness is critical to the performance and durability of the coatings, as thicker coatings can be prone to cracking. The maximum temperature at which TiN coatings can be used is 600 °C. Above this temperature, the coating can be damaged. Above this, the coating can be damaged. Choosing the right coating parameters is therefore crucial for optimum performance and durability of the coating.
Recommended layer thicknesses
The recommended layer thickness for TiN coatings is typically between 1 2 and 7 4 micrometers, depending on the material being processed. For special applications, it is recommended to use TiN coatings between 1 2 and 5 micrometers thick to achieve optimum results.
For use in machining, a coating thickness of 2 to 3 micrometers is often recommended to ensure optimum wear protection. This thickness offers high hardness and resistance, which are essential for metalworking.
The TiN coating gives surfaces a high hardness, which is typically around 2,000-2,300 HV. This hardness and stability make TiN an ideal material for various industrial applications.
Effects of layers that are too thick
TiN coatings that are too thick have a tendency to form undesirable cracks. This cracking can significantly impair the performance and durability of the coating, leading to premature wear of the tools.
The thickness of TiN coatings should therefore be in the range of 2 to 5 microns to ensure optimum results. Careful control of the coating thickness is crucial to achieve the best results and maximize tool life.

